Legacy Data Management is the comprehensive strategy and set of processes for handling data that resides on outdated or discontinued systems, formats, and applications. It involves securing, classifying, archiving, and potentially migrating this data to modern platforms to ensure its ongoing accessibility, compliance, and business value, while reducing the cost and risk associated with maintaining obsolete IT infrastructure.
What is Legacy Data Management?
In the lifecycle of any organization, technology evolves. Systems that were once cutting edge eventually become outdated, replaced by newer, more efficient platforms. However, the data generated and stored within these old systems often referred to as “legacy data” does not lose its value. This data can include critical business records, historical transaction details, customer information, intellectual property, and compliance related documents.
Legacy Data Management is the disciplined approach to dealing with this valuable yet challenging asset. It moves beyond simply “keeping the old server running” and instead focuses on a structured methodology. This process begins with identifying all legacy data across the enterprise, classifying it based on sensitivity and business value, and then determining the most appropriate action. The goal is to choose between secure archiving for long term retention, migration to a modern cloud environment, or secure disposal if it is no longer required.
The core challenge it addresses is that this data is often “locked in” siloed, unsupported systems. These systems are expensive to maintain, vulnerable to security breaches, and difficult to access for modern analytics and business intelligence. Effective Legacy Data Management liberates this data, transforming it from a technical liability into an accessible, secure, and usable resource that supports the organization’s current and future goals.
Why is Legacy Data Management Important?
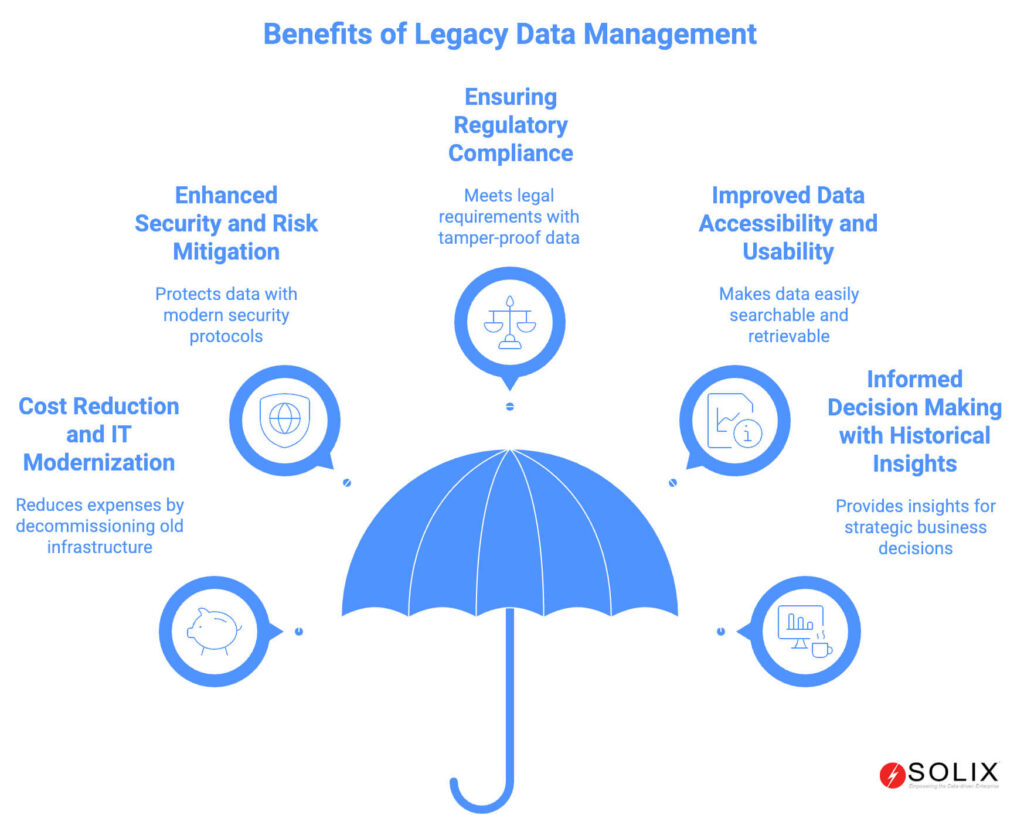
Ignoring legacy data is not an option for modern enterprises. The data held within these aging systems is often critical for regulatory compliance, historical analysis, and informed decision making. A proactive Legacy Data Management strategy is essential for mitigating risk, controlling costs, and unlocking hidden value. It is a fundamental pillar of a mature data governance program and a key enabler of digital transformation.
- Cost Reduction and IT Modernization: Maintaining legacy hardware and software is incredibly expensive. It requires specialized skills, consumes data center space and power, and often involves costly support contracts for obsolete technology. By archiving data from these systems, companies can decommission the old infrastructure. This leads to significant and immediate savings in hardware, software, and maintenance costs. This also frees up precious IT resources to focus on innovation and strategic projects rather than routine maintenance.
- Enhanced Security and Risk Mitigation: Out of support operating systems and applications no longer receive security patches. This makes them prime targets for cyberattacks and data breaches. Legacy data management involves migrating or archiving this data into secure, modern environments with robust security protocols, encryption, and access controls. This process drastically reduces the organization’s attack surface and protects sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: Industries like healthcare, finance, and the public sector are governed by strict data retention regulations. These include rules like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. Legacy data often falls under these mandates. Proper management ensures that data is retained for the required period in an immutable, tamper proof format. It can be produced quickly and accurately during audits or legal discovery. This proactive approach avoids substantial fines and legal penalties.
- Improved Data Accessibility and Usability: Data trapped in a legacy system is effectively dark data. It exists but cannot be used for any practical purpose. Modern legacy data management solutions provide indexed, searchable archives. This allows authorized users to easily find and retrieve specific records, emails, or files. They can do this without needing to restore an entire old system. This capability improves operational efficiency and customer service.
- Informed Decision Making with Historical Insights: Historical data contains invaluable patterns and trends. By bringing legacy data into a modern data lake or warehouse, organizations can perform longitudinal analysis. They gain insights that drive strategic business decisions, product development, and market positioning. Legacy data provides the context needed to understand long term trends.
Facilitating Smooth Mergers, Acquisitions, and Application Retirements: When companies merge or retire major applications like ERP or CRM systems, a vast amount of data must be consolidated and managed. A structured legacy data management process provides a clear framework for handling this data transition smoothly and efficiently. It ensures business continuity and preserves critical information assets during times of significant change.
Key Challenges and Best Practices for Businesses
Implementing a successful legacy data management program is not without its hurdles. Organizations often face a set of common challenges. Understanding these obstacles and adhering to established best practices is the key to a smooth and effective transition.
Common Challenges:
- Data Sprawl and Discovery: The first major challenge is simply finding all the legacy data. It can be scattered across physical servers, old tapes, individual hard drives, and forgotten cloud instances. Without a complete inventory, any management strategy will have gaps.
- Data Format and Compatibility Issues: Legacy data is often stored in obsolete or proprietary formats. Modern systems may not be able to read these formats natively. The challenge is to convert or emulate the environment to access the data without corrupting it.
- Understanding Data Context and Lineage: In old applications, data is meaningful because of its relationships and business context. Simply extracting raw tables is not enough. Preserving the metadata and the functional lineage, how data points relate to each other and business processes is critical for the archive to be useful.
- High Costs and Resource Drain: The perceived high upfront cost of a migration or archiving project can be a barrier. However, businesses must compare this one-time investment against the ongoing, and often rising, costs of maintaining outdated systems.
- Security and Compliance Risks: As mentioned, unpatched systems are a security nightmare. The challenge is to secure this data during the complex process of extraction, transfer, and loading into its new environment, ensuring no breaches occur in transit.
Essential Best Practices:
- Develop a Comprehensive Data Governance Policy: Before moving a single byte of data, establish a clear policy. Define what constitutes legacy data, set retention schedules based on legal and business needs, and assign clear roles and responsibilities for data ownership and management.
- Conduct a Thorough Data Audit and Classification: Use automated tools to discover and inventory all legacy data assets. Classify data based on its sensitivity, value, and retention requirements. This allows for prioritization and ensures that the most critical data is handled with the utmost care.
- Choose the Right Archiving and Migration Strategy: Not all data requires the same treatment. Determine whether data should be archived for compliance, migrated to a new active system, or defensibly disposed of. The right strategy depends on the data’s classification and business use case.
- Prioritize Data Security and Integrity: Ensure that the chosen solution provides end-to-end encryption for data both in transit and at rest. Implement strict access controls and maintain detailed audit logs to track every interaction with the data. Verify data integrity after migration to ensure nothing is lost or altered.
- Plan for Long Term Accessibility and Usability: An archive is only valuable if you can use it. Choose a solution that offers robust, easy-to-use search and retrieval capabilities. Ensure that the data format used for archiving is open or well documented to avoid future compatibility issues. Think of it as preserving not just the data, but the ability to understand it.
How Solix Helps Master Your Legacy Data
While the importance of legacy data management is clear, executing a successful strategy requires specialized expertise, robust technology, and a proven methodology. This is where Solix Technologies establishes its leadership. As a pioneer in enterprise data management solutions, Solix provides the comprehensive platform and deep industry experience necessary to turn the challenge of legacy data into a strategic advantage.
Solix understands that legacy data management is not a one time event but an ongoing program. The Solix Common Data Platform (CDP) is engineered to address the complex challenges and best practices holistically. Solix helps organizations not just by storing old data, but by actively managing it to deliver tangible business outcomes. The platform is designed to seamlessly implement the best practices that businesses strive to achieve.
How the Solix Common Data Platform Empowers Your Strategy:
- Comprehensive Application Decommissioning: Solix offers one of the industry’s most robust solutions for application retirement. We enable you to securely retire legacy applications like SAP ECC, Oracle E-Business Suite, and custom systems. This process preserves all related data and business context in a highly compressed, read only archive. This allows for full decommissioning of legacy hardware and software, achieving maximum cost savings. The platform solves the challenge of preserving data lineage and context, making archived information fully usable.
- Secure, Compliant Archiving: The Solix Enterprise Archiving solution provides a centralized, secure repository for all your structured and unstructured legacy data. With features like data encryption, immutable storage, and legal hold, Solix ensures your archived data meets the strictest compliance and governance standards. Your data is always ready for eDiscovery and audit requests. This directly addresses the critical needs for security and regulatory adherence.
- Structured Data Migration: When the goal is to modernize, Solix facilitates the seamless and accurate migration of legacy data to modern cloud environments like Azure, AWS, or Google Cloud. This ensures data integrity throughout the process, enabling a successful transition to new, agile platforms. Solix tackles the challenges of data format compatibility and integrity head on.
- Unlocking Data for AI and Analytics: Solix goes beyond simple storage. By consolidating legacy data into a unified platform, it can be cleansed, classified, and made available to feed modern analytics tools, Business Intelligence (BI) dashboards, and even AI and machine learning models. This transforms historical data from a static record into a dynamic asset for predicting future trends. It directly enables the business value of informed decision-making.
Solix Technologies is a leader in this space because we provide an end-to-end solution backed by a deep commitment to data security and compliance. Our platform is built to handle the scale and complexity of the largest global enterprises. This makes us a trusted partner for organizations looking to confidently modernize their IT landscape, reduce risk, and build a truly data-driven future. With Solix, you are not just managing your past; you are empowering your future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Legacy Data Management
What is an example of legacy data?
Legacy data can be customer records in an old custom built CRM system, financial transactions in a retired accounting application, patient files in a legacy healthcare database, or even emails from an outdated exchange server.
What is the best way to manage legacy data?
The best practice is to implement a structured legacy data management program that includes data discovery, classification, and then a decision to either archive, migrate, or dispose of the data using a dedicated platform like the Solix Common Data Platform.
What are the risks of not managing legacy data?
Risks include high maintenance costs, severe security vulnerabilities due to unpatched systems, non compliance with data regulations leading to heavy fines, and an inability to access critical business information for operations or legal discovery.
How does legacy data archiving differ from a backup?
A backup is a short term copy for disaster recovery, while archiving is the long term, secure preservation of inactive data for compliance and historical reference. Archives are indexed and searchable, while backups are not designed for frequent access.
Can legacy data be used for analytics?
Yes, and it should be. By migrating or consolidating legacy data into a modern data lake or warehouse, it can be analyzed alongside current data to uncover long term business trends and insights.
What is application decommissioning?
Application decommissioning is the process of retiring a legacy software application while securely preserving all its data in an accessible archive, allowing the organization to shut down the old system and stop paying for its maintenance.
Is legacy data management only for large enterprises?
No, businesses of all sizes accumulate legacy data. The principles of cost saving, security, and compliance apply to any organization that uses technology and generates data over time.
How does Solix ensure the security of my archived legacy data?
The Solix Common Data Platform employs enterprise grade security, including data encryption at rest and in transit, fine grained access controls, immutable storage to prevent tampering, and comprehensive audit trails to monitor all data access.